Arthrosis of the knee joint (deforming arthrosis of the knee joint, DOA, gonarthrosis) is called degenerative-dystrophic alteration of joint structures, in which the cartilaginous layer between the bone elements first thins and then collapses. In the early stages the patient feels discomfort and a slight limitation of mobility, then the joint deforms and, as the cartilage is destroyed, it completely loses its functions. Acute arthrosis is very painful and is accompanied by a significant decrease in the patient's physical activity. If treatment for gonarthrosis of the knee joint is not started on time, the patient may remain disabled.
For reference:According to statistics, one in five adults in the world suffers from arthrosis of the knee joint. Knee osteoarthritis can be unilateral or bilateral; In women the pathology is diagnosed twice as often as in men. People over the age of 45 often face the problem of joint deformation due to age-related changes in the body. If this diagnosis is made in young people, the cause is usually trauma.
Why does the pathology develop?
The knee joint is one of the most complex in the human body. Bears most of the load during walking and other movements. It is not surprising that with age its elements begin to wear out and lose their functions. First, the cartilage layer in the joint joint loses elasticity and elasticity, and then dries out and cracks. The shock-absorbing properties of cartilage are reduced, and it is precisely this that causes discomfort and pain during movement: shocks and impacts of the joint structures against each other are no longer attenuated by anything, the bones are gradually exposed and rub one against the other.
Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint in old age is an optional phenomenon, it is not diagnosed in everyone. There are a number of provoking factors, the combination of which causes pathological changes in the joint.
The most common causes of pathology are the following:
- excess weight – the joint must withstand additional loads;
- Osteoporosis is a pathology in which demineralization of bone tissue occurs;
- chronic diseases associated with metabolic disorders in the body;
- traumatic sports: gonarthrosis is often called the disease of football players due to frequent trauma to the knee joint;
- some types of professional activities associated with heavy physical activity - arthrosis and arthrosis - are found in loaders;
- spinal injuries in which the distribution of loads on the joints of the lower extremities is disrupted;
- hereditary predisposition.

Articular cartilage does not wear away immediately. In the initial stages, the manifestations of the disease are absent or insignificant, the patient does not consult a doctor and does not take any measures to stop the pathological process. But, if dystrophic changes are nevertheless identified, the patient has time to start treatment and prevent irreversible changes. To do this, you must first establish what the main signs of arthrosis of the knee joints are.
How to recognize the disease
Symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint become pronounced at the stage when the cartilage has already become thinner and has begun to deteriorate. Grade 1 gonarthrosis may not be felt for years. However, later, attentive patients remember that they still felt atypical symptoms, they simply did not attach much importance to them, since they were not constant and did not cause much discomfort.
You can suspect destruction and inflammation of the right or left knee joint based on the following specific signs:
- morning stiffness in the joint;
- limitation of mobility after a long stay in one position;
- knee discomfort when climbing stairs - burning sensation, hypersensitivity;
- night pain in the knees;
- pain after physical work or sport;
- periodic sudden weakness of the lower limbs. If right- or left-sided gonarthrosis develops, only one affected leg fails.
However, the main symptom of destruction of the knee joint remains pain. They can be of varying intensity and sometimes fade. But as the pathologies progress, they appear more often, become more intense and disturb the patient even at rest, in the absence of physical activity. Based on the severity of the symptoms, the doctor can diagnose the stage of the disease.
- Manifestations of stage 1 pathology:pain is not yet a cause for concern, the patient may notice rapid fatigue during sports practice or physical activity, a slight limitation of joint mobility after prolonged rest. An x-ray will show a slight narrowing of the space between the bones of the joint, an uneven surface of the cartilage with slight compactions.
- For 2 degree gonarthrosisthe symptoms appear brighter and more frequent. The patient usually already understands that something is wrong with his knees. Joints hurt and "twist" when the weather changes, after physical exertion. Even the gentlest movements cause knee pain. If a person lets his legs rest, the pain will disappear. But under load they will pick up again. Also at this stage of the pathology, a characteristic creaking of the knee may occur when bending and extending the leg, difficulty and pain when trying to bend the leg at the knee more than 90 degrees. An x-ray will show a change in the shape of the joint cup and the presence of fluid in the joint cavity.
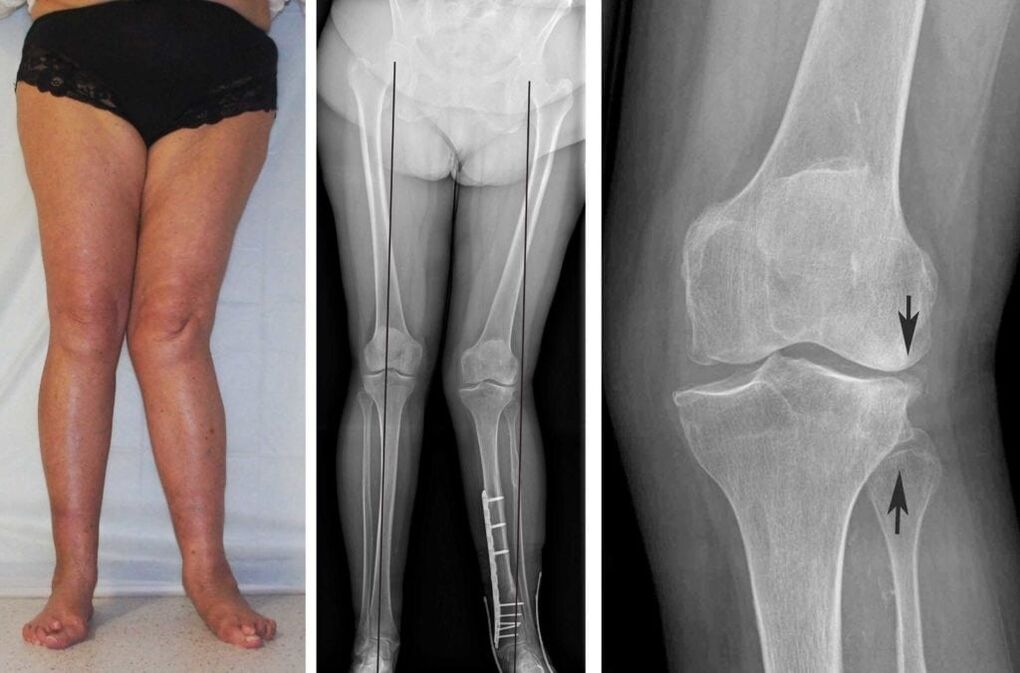
- Gonarthrosis 3 degreescharacterized by severe pain that occurs regardless of whether the limb receives a load or is at rest. The sore joint is especially painful at night and when weather conditions change. The patient is no longer able to bend his leg at the knee, which is why his physical activity and performance decrease. The x-ray clearly shows degenerative changes in the joint tissues. The deformation is also visually visible to the naked eye. The patient's legs are bent at the knees like the letter "o" or "x", which ultimately leads to the inability to move independently, without support, and even more so to carry out usual professional and household activities. The person becomes disabled.
Typically, patients consult a doctor in the second stage of the disease, mainly to find an effective medicine for knee pain. In the first stage, it is quite difficult to identify gonarthrosis, since the symptoms are mild and only small changes are visible on x-rays. It is possible to detect pathological changes in the joint only with a thorough examination.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis begins with a visual examination and questioning of the patient. What will indicate the possible development of gonarthrosis:
- widening and change in shape of the knee joint;
- a distinct creaking sound when the kneecap is moved;
- pain on palpation of the joint;
- limitation of joint mobility.
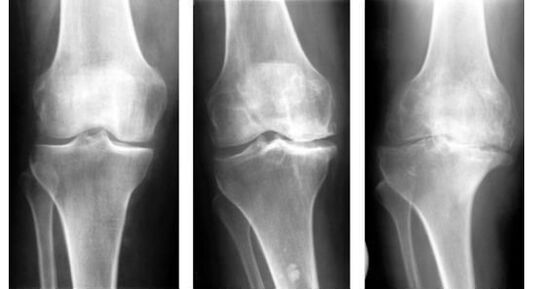
In the initial stages, degenerative changes in the cartilaginous tissue may not be visible, which is why CT and MRI are also recommended. With the help of modern diagnostic techniques, the doctor is able to accurately determine the severity of the joint, whether there is inflammation and accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity, and also differentiate arthrosis of the knee joint from other pathologies.
Classification
In modern orthopedics, there are two main types of arthrosis of the knee joints:
- primary gonarthrosis;
- secondary gonarthrosis.
The primary form of the disease develops on its own due to age-related changes or metabolic disorders. Secondary is a consequence of another disease, injury or unsuccessful surgery. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the knee joint can develop several months after a bruise, subluxation or fracture. Depending on the nature of the course, arthrosis is classified as acute or chronic. It is easier to cure the acute form of the disease.
Official medicine for gonarthrosis
Complex treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint begins only after final confirmation of the diagnosis. If the patient's condition is not critical, doctors will first try to stop the progression of the pathology with the help of drugs. Physiotherapy, massage and manual therapy are used as additional methods.
The main goals of complex therapy:
- relieve pain and discomfort;
- restore joint mobility;
- stop the destruction of the cartilage layer and, if possible, restore it.
Important points are physiotherapy and compliance with a special diet. There are exercises and products that work to restore damaged joint tissues and help to at least partially restore mobility. If you consult a doctor promptly, these measures are sufficient for the knee joint to begin to function fully again.
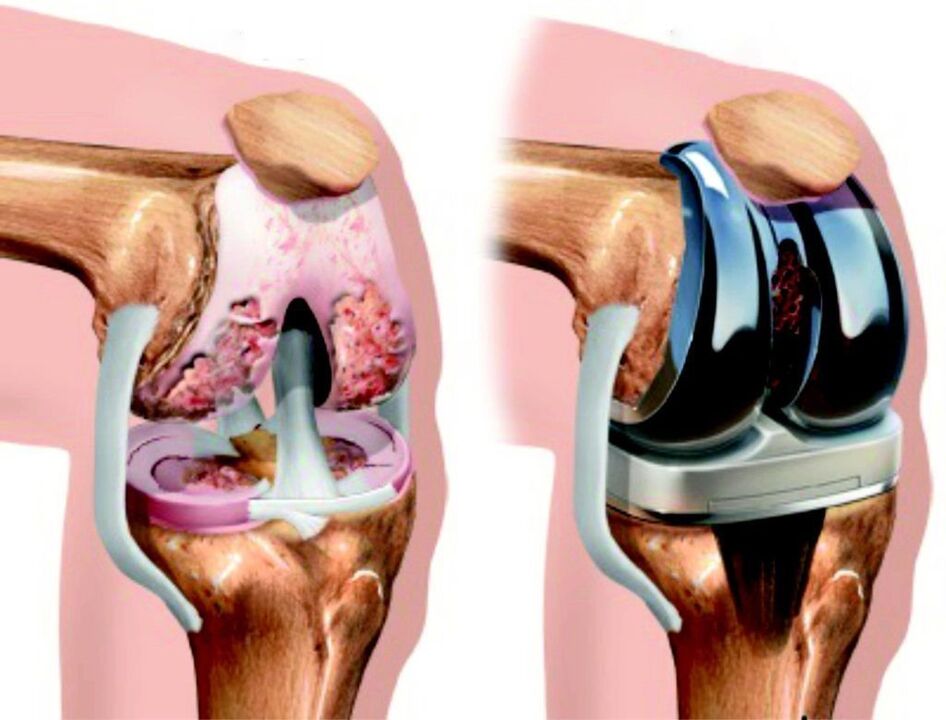
But if the disease has reached the third stage, the joint is severely damaged and even the most expensive drugs will not help restore it. Surgery will be necessary to preserve at least partial function of the limb. It consists of removing the remains of the affected joint structures and implanting an implant, the procedure is called endoprosthesis.
Pharmacological treatment of gonarthrosis
To eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, restore and strengthen the joint, a complex of drugs of various groups and actions is used.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs– joint treatment begins with them, they quickly relieve pain, swelling, fever and partially stop the inflammatory process. But they cannot be taken for a long time, since the active components in the composition have an extremely negative effect on the functions of the digestive tract and the composition of the blood. Usually, the course of treatment with NSAIDs lasts no more than 5-7 days. Medicines can come in the form of tablets for internal use or in the form of ointments and gels for external use.
- Chondroprotectors– these are drugs that improve the nutrition of the cartilaginous tissue and restore its compactness and elasticity. Chondroprotectors also partially relieve pain and swelling. But such drugs do not work immediately. The first effect will be noticeable a few weeks after starting the course of therapy. It is recommended to take chondroprotectors for at least six months.
- Hormonal drugs.They are also called corticosteroids. Hormone-containing drugs are used if the pain is very severe and the inflammation progresses even after a course of taking NSAIDs. They are administered as injections intramuscularly or directly into the joint cavity. Such drugs instantly relieve pain, reduce swelling and inflammation. But they have a number of contraindications and even more side effects than non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which is why they are prescribed in extreme cases. Hormonal drugs can be purchased in pharmacies only with a doctor's prescription. Immediately after the patient's condition improves, corticosteroids are stopped.
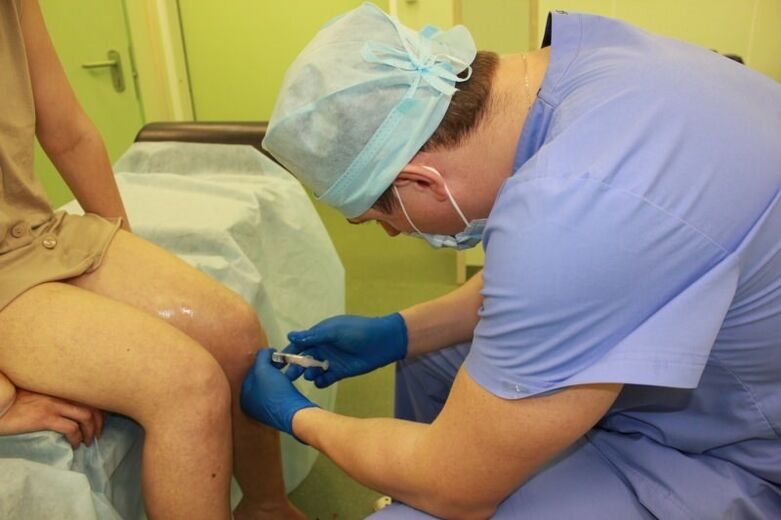
The treatment is completed by intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid. This substance stimulates the production of synovial fluid, saturates the cells with moisture, restores their elasticity, firmness and prevents abrasion. The cost of the procedure is quite high, but the effectiveness is worth the cost.
In a note:Of all the drugs listed above, only chondroprotectors affect the cause of the disease. They stimulate the regeneration of destroyed cartilage tissue and prevent damage to surviving cartilage cells. But these drugs are expensive, while to achieve a noticeable and lasting effect they must be taken regularly for several consecutive months, and sometimes even for years. The cost of comprehensive treatment for many patients, especially retirees, is often prohibitive.
Unconventional treatment methods
Patients who have experienced firsthand what knee arthrosis is and what unpleasant symptoms it manifests itself, always have several remedies available in case the pharmacy and medications are not available. People who suffer from gonarthrosis and knee pain prepare tinctures, rubs and ointments based on medicinal plants in advance: almost all recipes require time and fresh raw materials, available only in the spring-summer season.
Treatment with dandelion
There are several ways to strengthen the joint, restore its mobility and get rid of excruciating pain with the help of this medicinal plant. The simplest is to eat five dandelion heads every day during the flowering period. This should be done on an empty stomach, after rinsing the flowers with boiled water. A tincture for rubbing joints is also prepared from dandelions.
The cooking recipe is as follows:
- Collect exactly 50 open dandelion heads.
- Place in a dark glass bottle with an airtight cap.
- Pour 300 ml of good vodka or triple cologne.
- Infuse away from sunlight for a month, shaking the container from time to time.
- Without squeezing, transfer to the first aid kit, use before going to bed to massage the sore knee, then wrap the joint warmly and go to bed under a blanket.
There is another interesting recipe against arthrosis of the joints using dandelion. First you need to collect the leaves of the plant and dry them. Then pour boiling water and let it steam for half an hour. The resulting mixture must be chewed slowly and carefully for the time necessary to take exactly 3 thousand steps.

Recipes with burdock
The simplest recipe:
- collect two or three young leaves of the plant and rinse with cold water;
- Lightly crush the leaves to release the juice;
- Apply to the affected joint and secure with a bandage.
Keep this "compress" overnight, remove it in the morning and throw away the leaves. Repeat the procedure every day for three weeks.
To enhance the effect, traditional healers recommend lubricating the knee with cinquefoil oil before applying burdock. It is very easy to prepare. Two tablespoons of chopped cinquefoil are poured into 250 ml of any purified vegetable oil without fragrances. The oil should be preheated well, but not boiled. Leave the mixture for two weeks, then the oil can be used to treat joints.
Turpentine, eggs and other joint remedies
Using the yolk of a chicken egg, you can make an effective rub for sore joints. It is prepared like this:
- Lightly beat an egg yolk in a bowl.
- Add a teaspoon of turpentine and mix.
- Then pour in a generous spoonful of vinegar and beat again.
The mixture is stored in the refrigerator and used before bedtime. After rubbing, the knee is wrapped in a warm cloth overnight. In the morning you need to remove the bandage and rinse the remaining product with warm water, then apply any antiarthritic ointment.
Remember that all homemade preparations are effective only immediately after preparation, they are not stored for a long time (with the exception of tinctures with alcohol, they can be stored in a dark, cool place for up to six months). Don't expect immediate results. Folk remedies act on a cumulative system; Lasting relief will come only after three to four weeks of regular use of home remedies for knee osteoarthritis. In the later stages they will not be effective and will only help to temporarily reduce pain and swelling.
Summary:Osteoarthritis of the knee joint, or gonarthrosis, is one of the most common injuries of the musculoskeletal system in older people. In young people it occurs after an injury or during excessive physical exertion. The disease can be completely cured only in stages 1-2 with a competent and comprehensive approach. In the third phase, it is very often necessary to resort to an endoprosthesis to at least partially restore the functions of the limb and prevent complications.